In the assortment of our company there are several types and models of equipment designed to replace and help in the patient’s respiratory function.
A. Types:
- Stationary;
- Portable.
B. Type of air mixture supply:
- Centralized system;
- Balloon (for portable devices).
C. Application:
- anesthetic and respiratory;
- for carrying out resuscitation measures;
- combined (pain relief and artificial respiration).
D. Age groups of patients:
- intended for babies and children under one year old;
- for children from 1 to 6 years old;
- for children from 6 years old and adults.
E. Tidal volume and inspiratory rate:
- from 50 to 1500 ml (adults);
- from 20 to 300 ml (children);
- Adjustable from 10 ml to 3000 ml.
F. Inspiratory frequency:
- from 4 to 100 bpm;
- from 1 to 40 bpm in SIMV mode.
G. Humidification:
- Respiratory mixture;
- Mucus aspirator.
H. Alarms:
- Apnea;
- Low or high pressure;
- Power failure / low battery.
I. Indicator of minute ventilation to the maximum:
- From 40-50.
J. Positive inspiratory pressure upper level:
- 60-100 hPa.
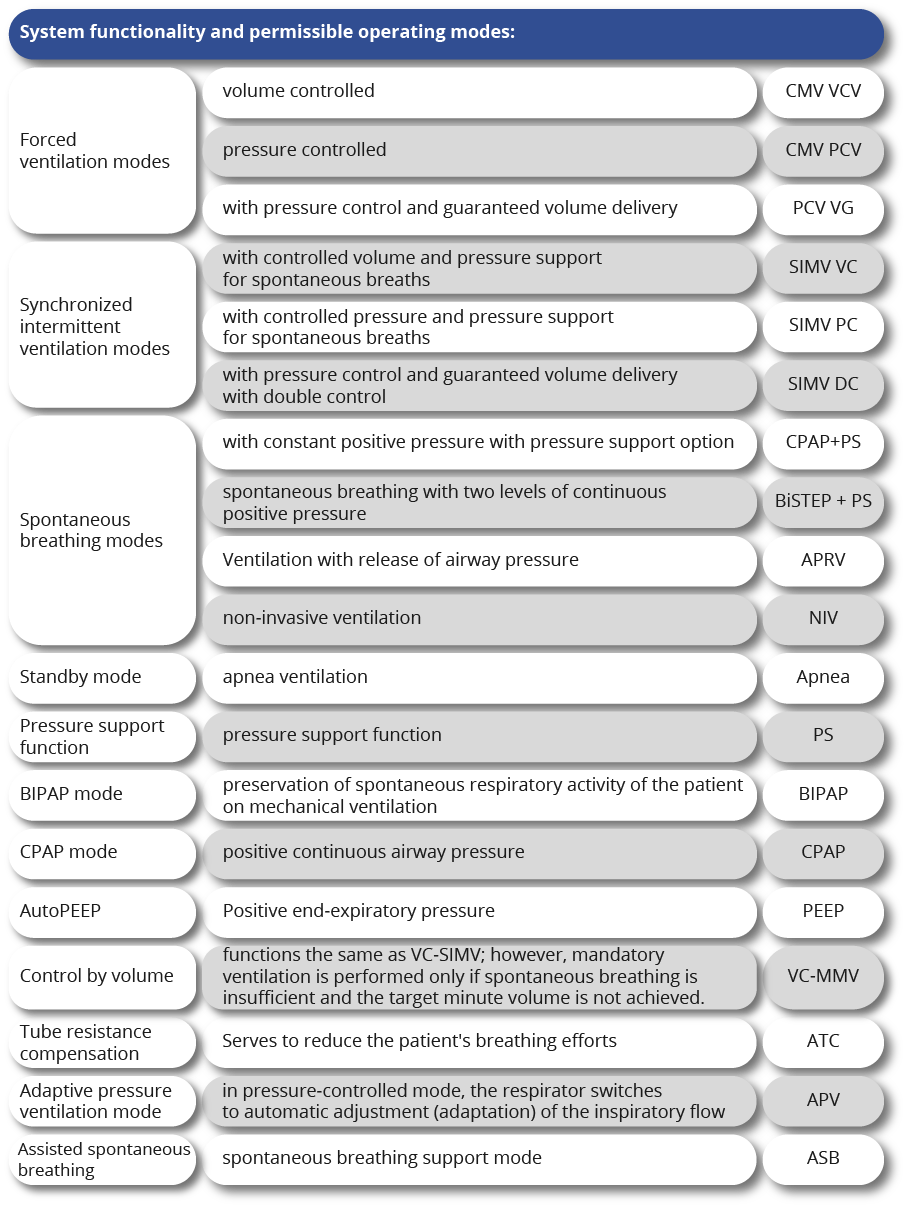
IMV – Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation Algorithm
IPPV – intermittent ventilation mode under positive pressure (analogue CMV)
MMV – guaranteed minute ventilation mode
MRV – ventilation at a given frequency (analogue of Volume Support)
PAV – proportional auxiliary ventilation mode
PLV – pressure limited ventilation mode
PPS – proportional pressure support mode (analogous to PAV)
Pressure Augmentation – mode with pressure build-up (analogue of VAPS)
Pressure Control – pressure-controlled ventilation mode
PRVC – pressure controlled volume mode
PS – pressure support mode
PSV – pressure support ventilation mode (similar to Pressure Support)
PSVG – ventilation mode of variable pressure support with guaranteed tidal volume (analogue of Volume Support)
SIMV – synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation algorithm
SPAP – spontaneous positive airway pressure (similar to BIPAP, not to be confused with CPAP!)
TGI – Trachea Injection Mode
VAPS – Volume Guaranteed Pressure Supported Mode
VPS – ventilation mode of variable pressure support (analogue of Volume Support)
Volume Assist – Volume Support (PAV Mode Option)
Volume Control – ventilation mode controlled by volume
Volume Support – volume support mode
VV + – advanced volumetric ventilation mode (analogue of PRVC)

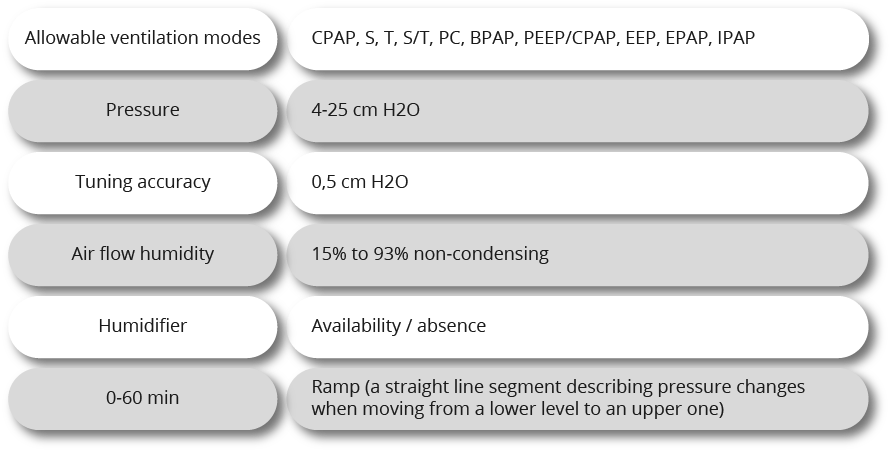
Designed to supply air under sufficiently strong pressure, which does not allow the soft structures of the pharynx to close and does not allow breathing to stop. This equipment is used mainly for obstructive sleep apnea.
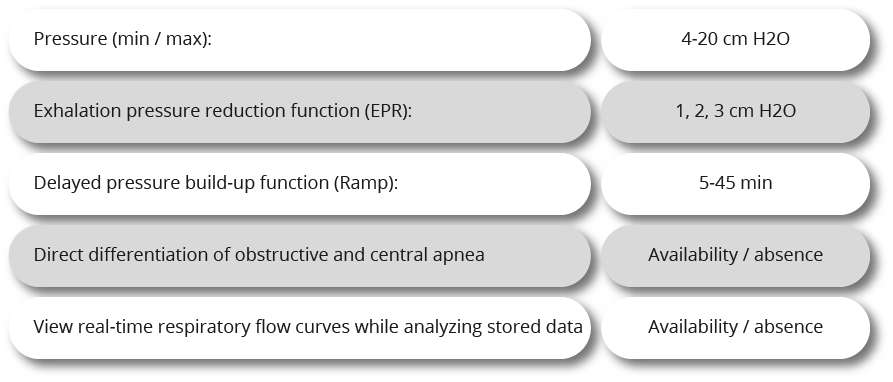

BIPAP generates different pressures for inhalation and exhalation. Due to this, it is possible to set the values of therapeutic pressure in the inspiratory phase, significantly exceeding the maximum possible with CPAP therapy.
The scope of BIPAP equipment is wider than that of CPAP. It is used in cases when the lungs do not receive sufficient volume of oxygen for full gas exchange, regardless of the presence / absence of obstruction.
Prices